On February 27th, the High Technology Research and Development Center of the Ministry of Science and Technology held a press conference in Beijing to release the top ten progress of China's science in 2017.
The “Top Ten Progress of Science in China†was organized by the Basic Research Department of the Ministry of Science and Technology and the High Technology Research and Development Center (Basic Research Management Center) of the Ministry of Science and Technology. It aims to implement the strategy of innovation-driven development in an in-depth manner and give full play to technological innovation in comprehensive innovation. Leading role, promoting science, advocating innovation and pursuing excellence in scientific innovation. It has been held for 13 sessions as of February 2018.
The top ten progress selection activities of China Science are sponsored by the High Technology Research and Development Center of the Ministry of Science and Technology, and five editorial departments such as China Basic Science, Science and Technology Herald, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China Science Foundation, and Science Bulletin. Co-organized. The selection process is divided into three stages: recommendation, primary selection and final selection. Among them, more than 2,000 experts including the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Chinese Academy of Engineering, and the director of the State Key Laboratory participated in the final online voting.
1. Realize thousands of kilometer-scale quantum entanglement and key distribution and teleportation
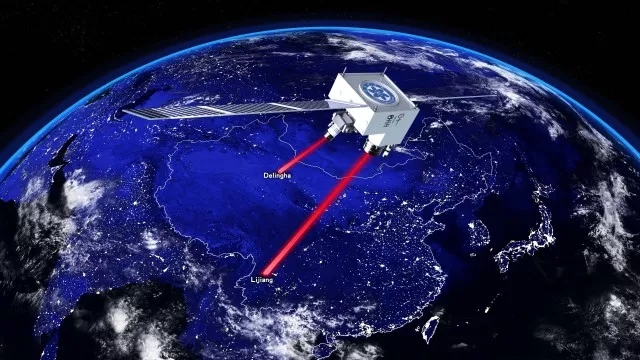
The "Mozi" quantum science experimental satellite was the first space quantum science experimental satellite in the world independently developed by China. It was launched on August 16, 2016, and completed on-orbit test on January 18, 2017. Conduct scientific experiments. The research team of Pan Jianwei and Peng Chengzhi of the University of Science and Technology of China and the Wang Jianyu Research Group of the Shanghai Institute of Technical Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have innovatively broken through the two-way high-precision light tracking and space, high-brightness quantum entanglement source, and the anti-intensity fluctuation decoy. Quantum light source and space-based long-life low-noise single-photon detection and other international leading key technologies, using the "Mozi No." to take the lead in realizing the two-dimensional quantum entanglement distribution of thousands of kilometers of stars, and on this basis to achieve spatial scale Strictly satisfying the non-locality test of quantum mechanics of "Einstein locality condition"; realizing the quantum key distribution of thousands of kilometers of stars and the teleportation of geostrophic quantum, the key distribution rate is higher than the ground distance optical fiber quantum communication The level has increased by 20 orders of magnitude, providing reliable technical support for the construction of a globally integrated quantum secure communication network covering the whole world. It has laid a solid foundation for China to continue to lead the world in quantum communication technology development and spatial scale quantum physics fundamental research. Science and technology foundation.
Relevant research progress was published in Science, June 16, 2017 [Science, 356 (6343): 1140-1144] and September 7, 2017, Nature (Nature, 549 (7670): 43-47] and [Nature, 549 (7670): 70-73]. After the publication of the research results, it has attracted extensive attention from the international academic community and the news media. It has also been highly praised by the international academic community. It was selected as the “2017 major scientific event†selected by Nature magazine and the famous American scientific media Science News. ". Professor Pan Jianwei, the chief scientist of "Mozi", was also selected by Nature magazine as "the top ten scientific figures in the world of change in 2017", which is called "the physicist who makes quantum communication between the heavens and the earth."
2. Convert the virus directly into live vaccines and therapeutic drugs
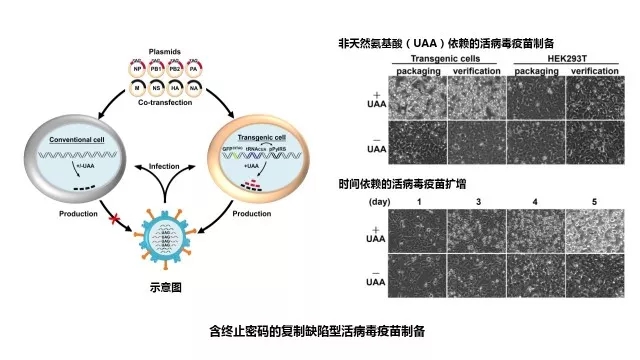
Infectious diseases such as influenza, AIDS and Ebola hemorrhagic fever are endangering human health and social stability. The behind-the-scenes "black hand" is a virus with structural and versatile and rapid mutations, and vaccines are an effective means of preventing viral infections. Peking University School of Pharmacy Zhou Demin and Zhang Lihe's research group used influenza virus as a model. Under the condition of retaining the complete structure and infectivity of the virus, only a triple genetic code of the mutant virus gene was used as the stop code, and the influenza virus was infected by pathogenicity. The source becomes a preventive vaccine, and then the multiple triplets are mutated to terminate the password, and the virus becomes a therapeutic drug. These vaccines are characterized by retaining the entire antigen, infection activity and the same infection pathway of the wild-type virus, which can induce strong and humoral immunity, nasal mucosal immunity and T-cell activation immune response, but replicate after infection in humans. Lack of ability. This replication-defective live virus vaccine has been validated in a mouse, ferrets and guinea pig model for broad-spectrum, long-lasting and efficient results. This method subverts the concept of traditional inactivated/attenuated vaccines. The former needs to change the structure of the virus antigen to remove its toxicity, which can only partially stimulate the body's immunity, so it needs multiple vaccinations. The latter requires complex processing to retain the intact structure of the virus, but still has weak replication ability and potential pathogenicity, and has a large safety hazard. This method will be a common method for developing live virus vaccines and can target almost all viruses.
Related research progress was published in the December 2, 2016 issue of Science [Science, 354 (6316): 1170-1173]. The research progress is a typical example of China's long-term support for basic research and encourages basic research for clinical transformation. Science magazine reviewed the development as a revolutionary breakthrough in the field of viral vaccines, which Nature called "a new way to tame the virus."
3. The first detection of the double-barrel
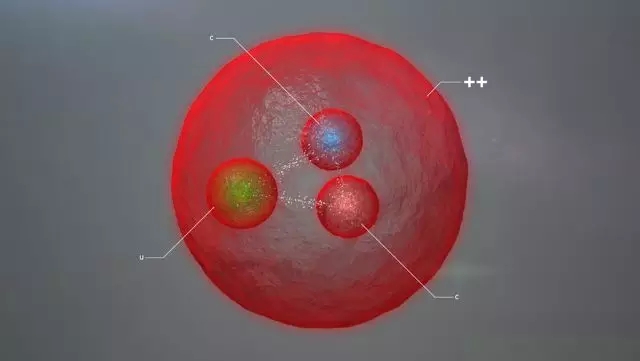
The CERN announced on July 6, 2017 that scientists from the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) Upper Base Quark Detector (LHCb) International Cooperation Group have discovered a new particle called the scorpion baryon. The particle has two unit charges and has a mass of about 3621 megaelectron volts, which is almost four times the mass of the proton. Similar to protons and neutrons, the newly discovered scorpion baryon is composed of three quarks, but its quark components are different: protons consist of two upper quarks and one lower quark, and neutrons consist of two lower quarks and one upper quark. The double-tweezers are composed of two heavier ç²² quarks and one upper quark. The theory predicts that the internal structure of the big scorpion is different from the previously discovered particles, and the study of its properties will help humans to understand the composition of matter and the nature of strong interaction.
Related research progress was published in the September 11, 2017 issue of Physical Review Letters, 119, 112001. The Endquake Detector International Cooperation Group consists of more than 1,000 scientists from 16 countries. Tsinghua University, Central China Normal University, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences and Wuhan University are members of the cooperation group. The Chinese research team led by Tsinghua University's Highlands Ning has led the physical analysis of the discovery of the scorpion, and has made a key contribution to the discovery of the particle by working closely with domestic theorists. The CERN has made a special press release on the discovery of Shuangzi, and has been reported by the global media. The reviewer commented: "The paper gives the long-awaited important results - the first observation of the double-barreled baryon." The US "Physics" magazine also featured a monograph on "multiple fascinating particles". It was found that “providing researchers with a unique system for testing quantum chromodynamicsâ€.
4. Experiments found triple degenerate fermions
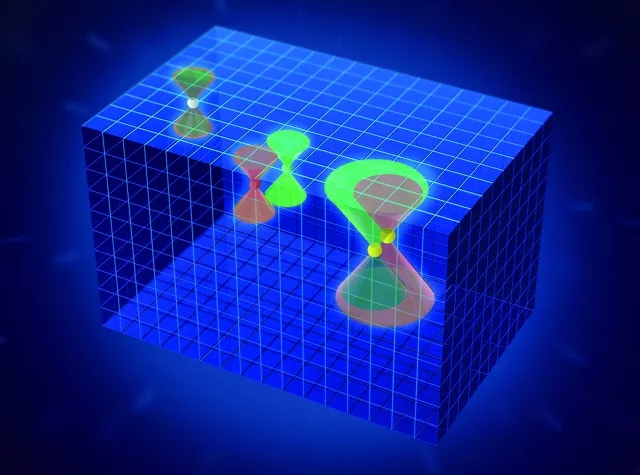
The basic particles that make up the universe can be divided into bosons and fermions. The current theory holds that there are only three types of fermions in the universe, namely Dirac Fermi, Del Fermi and Mayorana Fermi, among which Dirac Fermi has quadruple degeneracy, and the fermion. There are two degeneracy with the Mayorana Fermi, and the triple degenerate Fermion does not exist in the universe. These three types of fermions can also exist in solid materials in the form of quasi-particles. The existence of Dirac fermions and ferm fermions has been experimentally confirmed, and the Mayorana fermions have also been experimental. stand by. These solid materials are colloquially referred to as "solid universes" and correspond to the real universe. Unlike the cosmic space of time and space, the "solid universe" only satisfies the discrete symmetry of discrete spaces, which may lead to new fermions that do not exist in the real universe. The search for a new type of fermion in the "solid universe" is a challenging frontier scientific issue in the field of condensed matter physics in recent years, and is also one of the focuses of international competition in this field. Ding Hong, Qian Tian and Shi Youguo, research fellows and collaborators of the Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, used angle-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy techniques in the Shanghai Light Source “Dream Line†and Swiss light source to observe a class in the phosphide crystal. Triple degenerate ferm. This is the first experiment to find a fermion beyond the traditional Dirac/Eur/Majorana type. Their experimental findings open up the way to explore non-traditional fermions in condensed matter systems, which is of great significance for promoting people's understanding of quantum states, discovering novel physical phenomena, and developing new electronic devices.
Related research progress was published in the June 29, 2017 issue of Nature [Nature, 546 (7660): 627-631].
5. Realize low temperature preparation and storage of hydrogen
Hydrogen is known as the next generation of secondary clean energy, but the efficient preparation of hydrogen and safe storage and transportation have long been a bottleneck that hinders the large-scale application of hydrogen energy. Since methanol can be transported safely, hydrogen is stored in liquid methanol, and hydrogen is produced in situ by water and methanol low-temperature liquid phase reforming reaction. When hydrogen is stored in methanol, it also activates equimolar water to release additional Hydrogen is a viable way to utilize hydrogen. The process device is simple, low in energy consumption, and easy to integrate with an on-board or fixed polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell, and the hydrogen-to-weight ratio released can reach 18.8%. Research by Martin Research Group of the School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering of Peking University and Wen Xiaodong of the Shanxi Institute of Coal Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Ishikawa of Dalian University of Technology, etc., have shown that platinum monoatoms are dispersed on a face-centered cubic structure of molybdenum carbide (α-MoC). The catalyst can be used for liquid phase reforming of methanol and exhibits high hydrogen production activity at lower temperatures (150-190 degrees Celsius) up to 18,046 moles per hour of platinum. This superior hydrogen production capacity is much greater than previously reported low temperature methanol reforming catalysts (up to nearly two orders of magnitude higher), the key to which is the ability of α-MoC to dissociate water and the synergistic activation and reorganization of platinum and α-MoC. The ability of methanol. At the same time, the research team also broke through the problem of high reaction conversion rate and high reaction rate under low temperature conditions in the process of water gas shift hydrogen production (CO+H2O=CO2+H2), and developed based on Au/α-MoC. A new generation of catalytic processes.
Relevant research progress was published on April 6, 2017, Nature, 544 (7648): 80-83, and July 28, 2017, Science [Science, 357 (6349): 389-393]. . The above research progress has been reported and highly praised by many scientific media. The American Chemical Society C&E News magazine and the British Royal Chemical Society Chemistry World magazine respectively use "hydrogen energy: a new process for preparing hydrogen fuel" and "a new catalyst to illuminate the future of hydrogen energy vehicles" A highlight of the issue was that "with the success of this highly active catalytic system, the concept of storing hydrogen in methanol and reforming it when needed may be practical, which is a major part of hydrogen storage and transport systems. breakthrough".
6. Developed a new generation of ultra-high strength steel based on coherent nano-precipitation strengthening
Ultra-high-strength steel plays a supporting role in important areas of national economy such as aerospace, transportation, advanced nuclear energy and national defense equipment, and is also a key material for future lightweight structural design and safety protection. However, for decades, the research on high-performance ultra-high-strength steel has always been based on the traditional semi-coherent precipitation to produce strong coherent distortion. There are inherent defects in the number of precipitated phases, unreasonable precipitation size and uneven distribution, which reduces The plastic toughness of the material seriously affects the safety of service. In addition, the expensive preparation cost also limits its practical application and becomes a problem that plagues the development of the high-end steel industry. Lv Zhaoping, research group and collaborators of Beijing University of Science and Technology, aimed at the goal of low-cost and high-performance, and innovatively proposed the design idea of ​​using high-density coherent nano-precipitates to strengthen ultra-high-strength alloys, using light and cheap aluminum instead of horses. The expensive cobalt and titanium elements in the aging steel greatly reduce the cost and promote the precipitation of extremely high density and full coherent nanophase by simple heat treatment, and develop a new generation of ultra high strength steel with coherent nano-precipitation strengthening. By regulating the lattice mismatch, the precipitated phase produces extremely low coherence distortion while having high order resistance, which greatly enhances the strength of the alloy without sacrificing its ductility. The subversive alloy design ideas involved can also be applied to the development of other structural materials.
Related research progress was published on April 27, 2017 in Nature (Nature, 544 (7651): 460-464]. According to a special review article published by Nature Materials, the study "excellent strength, plasticity and cost for research and development with the perfect super martensitic steel design concept, simplified alloying elements and precipitation phase strengthening essence. The combination of structural materials provides a new way."
7. Preparation of multi-particle entangled states by quantum phase change determinism
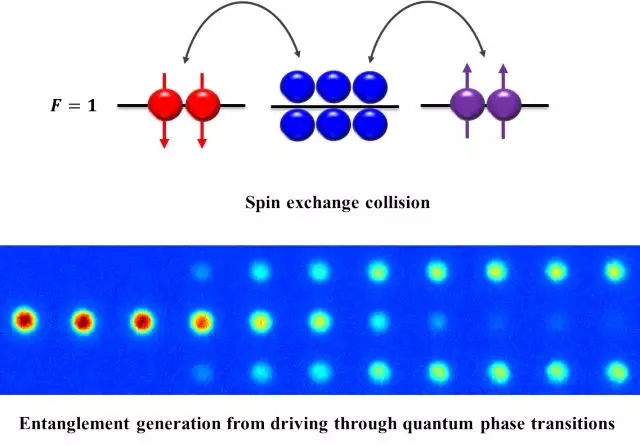
The realization of multi-particle entanglement is a major pursuit of quantum physics experiment research. The research group of the Department of Physics of Tsinghua University, You Li and Zheng Mengyu, through the spin mixing process in the Bose-Einstein condensate of the 铷-87 atom, causes two consecutive quantum phase transitions to achieve about 11,000 atoms. Deterministic preparation of the double number state. By directly observing the entangled state, they characterize the difference of the atomic number between different internal states with a lower than the classical limit of 10.7±0.6 dB, and the normalized length of the collective spin is approximately perfect 0.99±0.01. These two indicators reflect that the multi-body entangled state can provide phase measurement sensitivity of approximately 6 decibels beyond the standard quantum limit, and at least 910 entangled atoms - creating a world record for the number of quantum entangled particles currently deterministically prepared. The deterministic preparation of multi-body entangled states by quantum phase transition is a new attempt. Since the energy gap of a finite system at a continuous quantum phase transition point is small, a large excitation occurs when the system passes through the phase transition point. Their research shows that even if this excitation occurs, the multi-body structure of the quantum phase transition point can help to produce high-quality multi-particle entangled states. This new understanding and entangled state preparation method provides an idea for the preparation of other multi-particle entangled states in the future. In addition, the deterministic preparation of the double-numbered states is a practical development of measurement science and technology beyond the standard quantum limit, such as atomic clocks and atomic interferometers that achieve Heisenberg's limit accuracy.
Related research progress was published in the February 10, 2017 issue of Science [Science, 355 (6318): 620-623].
8. China discovered new ancient human fossils
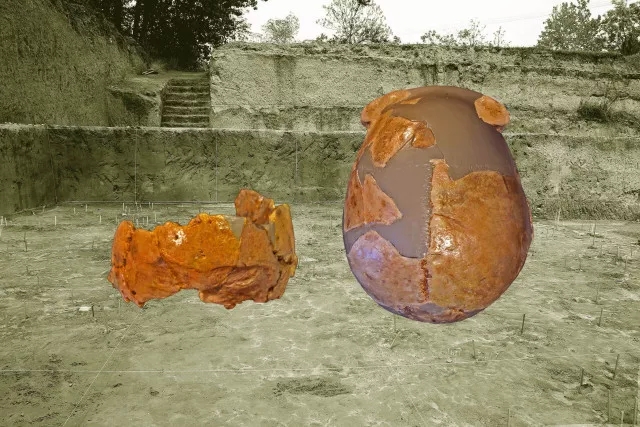

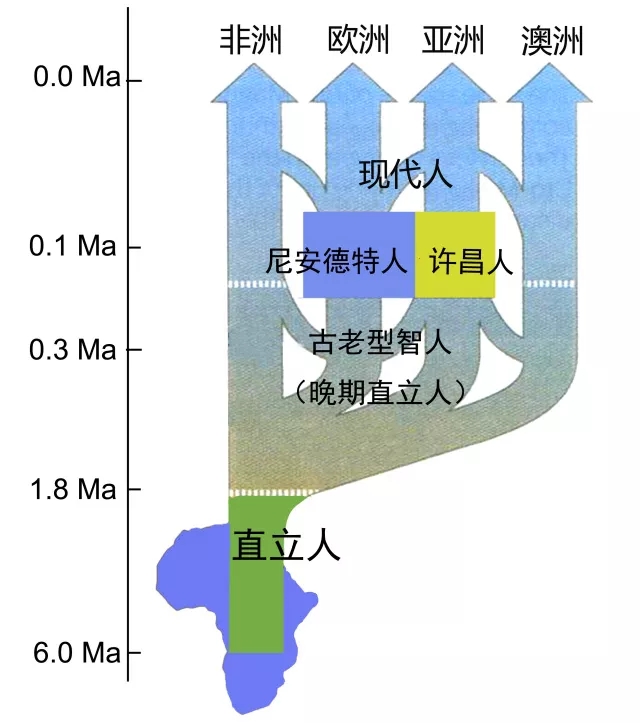
For a long time, the ancient anthropological community has been controversial about the evolutionary status of ancient human members in the transitional period from the late Middle Pleistocene to the late Pleistocene in China. The focus of the debate is: Are they evolved from the local ancient humans? Or is it a successful intruder from a foreign population? The two ancient humans, the Xuchang people's skull fossils, discovered recently at the Lingjing site in Henan Province, provided important information for exploring the evolutionary patterns of ancient Chinese humans at this stage. Research by Wu Xiujie, researcher of the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Erik Trinkaus of the University of Washington in the United States have shown that the Xuchang human skull has both low-lying cerebral palsy, flat cranial sagittal plane, and maximum cranial width. The ancient features of the lower position, while at the same time having the occipital bones (the occipital pillow/concave shape) and the inner ear labyrinth (semi-regular tube) form in the western Eurasian continent, showing the regional continuity of evolution and Dynamic changes in inter-regional population exchanges. In addition, Xuchang people's large brain volume (1800 cc) and the thin brain structure reflect the general trend of the evolution of human biological characteristics in the Middle Pleistocene. It is currently impossible to classify it into any known ancient human member, and Xuchang may represent a new type of ancient human. This study fills the gap in the evolution of ancient Chinese humans from the transition of ancient humans to early modern humans, indicating that there may be many ancient human members in the early Pleistocene, and there are hybrids or gene exchanges between different groups. The Xuchang people's fossils provide a certain degree of support for the regional continuity of the evolution of ancient Chinese humans and the exchanges with ancient European humans.
Related research progress was published in the March 3, 2017 issue of Science [Science, 355 (6328): 969-972]. The research findings have attracted great attention from academic circles and media at home and abroad. Science, Current Biology and other international top academic journals have published special comments on this topic, arguing that this research fills the transition period between ancient humans and early modern people in East Asia. The blank of human evolution is a major breakthrough made by Chinese scholars in the field of ancient human research.
9. Precision custom synthesis of yeast long chromosomes
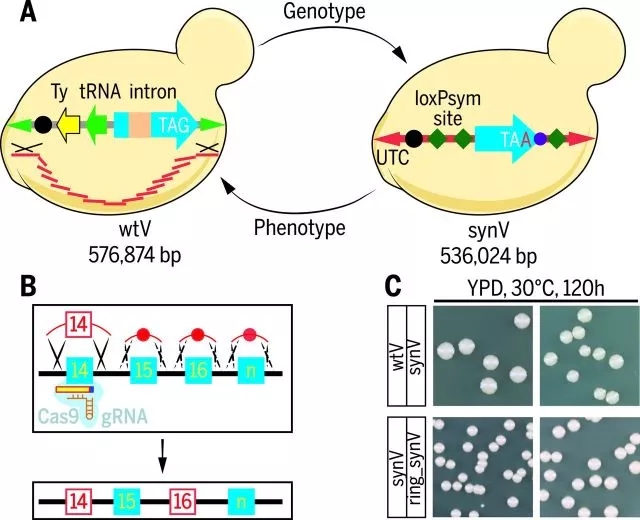
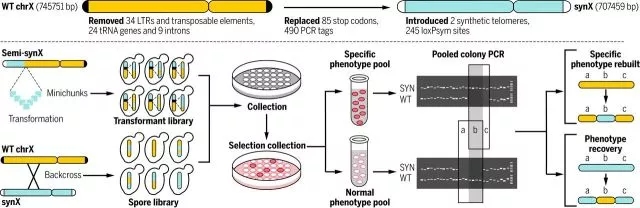
Genomic design and synthesis is a new design and de novo construction of the genome, capable of shaping life on demand, opening the door to the transformation from non-living matter to living matter, and promoting life science research from understanding life to creating life. However, the combination of genes is difficult to accurately synthesize long chromosomes, and to synthesize chromosomes to cause cell inactivation. Teams and collaborators of Tianjin University Yuan Yingjin, Tsinghua University Dai Junyi, Shenzhen Huada Gene Yang Huanming and so on use multi-level modularization and standardized artificial gene combination methods, based on one-step large fragment assembly technology and parallel chromosome synthesis strategy, realized by small The customary synthesis of molecular nucleotides to living eukaryotic long chromosomes, the establishment of a precise repair technology based on multi-target fragment co-transformation and the repair of large DNA fragments, successfully designed and constructed four long chromosomes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The exact match between the eukaryotic long chromosome synthesis sequence and the designed sequence; the rapid establishment of the genomic defect target rapid localization method was established, and a new strategy of phenotypic and genotype association analysis was provided, which was solved by the location and elimination of the defect target. Synthetic genomes lead to the problem of cell inactivation; on this basis, artificial circular chromosomes are constructed, which establishes a research model for the mechanism and potential therapeutic methods of currently unrecognizable chromosome-forming diseases. This research provides new ideas for deepening understanding of basic scientific issues such as life evolution, genomic and functional relationships.
The relevant research progress was published in four papers on March 10, 2017, Science [Science, 355 (6329): eaaf 4704, eaaf 4706, eaaf 4791, eaaf 3981]. The research results have attracted great attention from experts and media at home and abroad. Science published a review of the same period, and several top journals such as Nature, Nature Biotechnology, Nature Reviews Genetics, and Molecular Cell published special articles or highlights. The work was highly regarded as an important milestone in the first fully synthetic eukaryotic genome.
10. Developed a miniature microscopic imaging system that enables free-state brain imaging
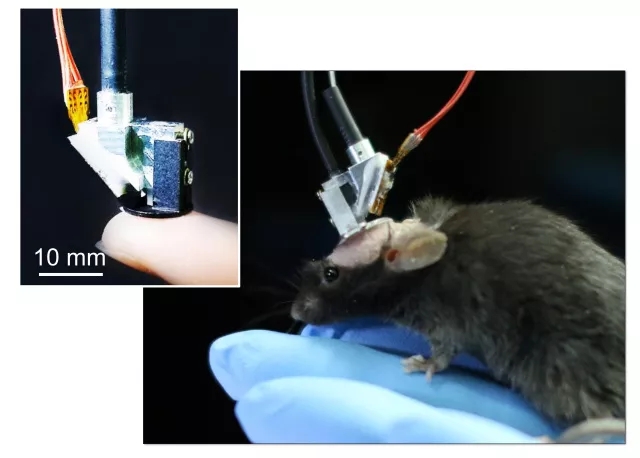
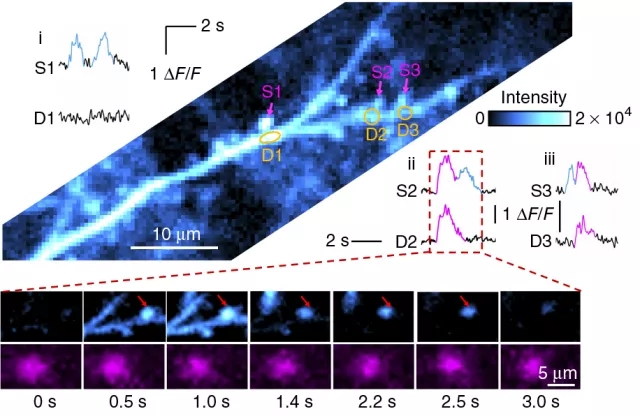
Cheng Heping and Chen Liangyi, National Key Laboratory of Biofilm and Membrane Bioengineering, Peking University, and Zhang Yunfeng and Wang Aimin, School of Electronic Engineering and Computer Science, use micro-integration, micro-optics, ultra-fast fiber lasers and semiconductor optoelectronics. High-temporal resolution has made breakthrough technological innovations in the development of volume imaging systems, and successfully developed a 2.2-gram miniaturized wearable two-photon fluorescence microscope. The first time in the world, the mouse brain was recorded under natural behavior conditions such as tail suspension, jumping platform and social interaction. High-speed, high-resolution images of neuronal and synaptic activity. This breakthrough technology will open up new research paradigms to achieve long-term observations of multi-scale, multi-level dynamic information processing of synapses, neurons, neural networks, and multiple brain regions under natural animal behavior. Not only can you "see" the process of brain learning, memory, decision-making, and thinking, but it will also play an important role in visualizing the neural mechanisms of brain diseases such as autism, Alzheimer's disease, and epilepsy.
Related research progress was published in July 2017, Nature Methods, 14(7): 713-719. The imaging system was called a revolutionary new tool for studying the spatial localization of the brain's nervous system by Edvard I. Moser, winner of the 2014 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.
Attachment: Ten Progresses in Chinese Science in the Past Five Years
2016
1. Developed a new cobalt-based electrocatalyst that converts carbon dioxide efficiently into a liquid fuel;
Second, create a new shortcut for coal to olefins;
3. Molecular genetic mechanism revealing the heterosis of rice yield traits;
4. A new method of tumor immunotherapy based on cholesterol metabolism regulation is proposed;
5. Reveal the key molecular mechanisms of RNA splicing;
Sixth, found that sperm RNA can be used as a memory carrier to inherit sexual traits across generations;
7. Developed the first stable and controllable single-molecule electronic switching device;
8. Build the world's first non-human primate autism model;
9. Reveal the epigenetic regulation mechanism of key signaling pathways during embryonic development;
X. Reveal the nuclear quantum effect of water.
2015
First, realize the single photon multi-free metric substealing state;
Second, theoretical prediction and experimental verification of the presence of foreign semi-metals;
3. Reveal the evolution of Ebola virus and its genetic diversity;
Fourth, to achieve the measurement of the interaction between antimatter;
5. Detecting the most quasar of the black hole in the brightest center of the universe;
6. Discover the earliest modern human fossils in East Asia;
7. Reveal the gene expression and epigenetic regulation characteristics of human primordial germ cells;
8. Analyze the key molecular mechanisms of cellular inflammatory necrosis;
Nine, developed a carbon-based high efficiency photolysis water catalyst;
X. Realize magnetic resonance detection of individual protein molecules.
Year 2014
I. Elucidation of the signaling pathways of monosodium lactone to regulate rice tillering and plant type;
Second, the newborn heart was found to have the ability to regenerate coronary arteries;
Third, propose and verify a planting mode that can both increase production and reduce environmental costs;
4. Using a solution method to prepare a high performance quantum dot light emitting diode;
5. Synthesizing nano twinned diamond with unprecedented hardness and thermal stability;
6. Propose and confirm that polar body transplantation can effectively block the transmission of mitochondrial genetic diseases;
7. Using the high-throughput sequencing results of polar bodies to accurately derive maternal genomic information;
8. Confirm that the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau expands eastward through the lower crust material flow and the upper crust along the fault block slip;
Nine, using nano-limited single-iron catalyst to achieve direct gas production from ethylene;
X. It was found that inflammatory caspase is an innate immune receptor for intracellular bacterial lipopolysaccharide.
year 2013
1. Chinese scientists have actively made important progress in responding to the new H7N9 avian influenza virus;
Second, the quantum anomalous Hall effect observed in magnetic topological insulators; Tsinghua University;
3. Direct observation of intermolecular hydrogen bonds using an atomic force microscope;
4. Beijing Spectrometer III observed a charged particle containing at least 4 quarks;
5. The drafting of wheat A genome and D genome is completed;
6. Inducing the transformation of mouse somatic cells into pluripotent stem cells using small molecule compounds;
7. Synthesize superhard nano twin crystal cubic boron nitride;
8. Developed a phase change metal nanocomposite with large elastic strain, low modulus and high strength;
9. Single-molecule chemical imaging based on plasmon-enhanced Raman scattering;
X. The astrocyte dopamine D2 receptor was found to inhibit neuroinflammation by αB crystal globulin.
2012
1. Shenzhou 9 and Tiangong No. 1 successfully realized the manned rendezvous and docking;
Second, scalable quantum information processing has made a series of important advances in the University of Science and Technology of China;
3. Explain the mass extinction of the turn of the Permian-Triassic and its recovery mode and causes;
Fourth, the Daya Bay neutrino experiment found a new neutrino oscillation mode;
5. Revealing the mechanism by which two natural products target specific proteins to treat leukemia;
6. Confirming that the haploid orphan male stem cells have the ability to replace sperm and rapidly transmit genetic modification;
7. Ecological experiments have confirmed that Bt transgenic cotton planting can promote biological control of pests;
8. Analyze the structural basis of the TAL effector protein to specifically recognize DNA;
Nine, revealing the molecular mechanism of autophagy induced by nutrient deficiency;
X. It was found that the energy conversion efficiency of the polymer solar cell can be improved by using the inverted structure.
Our withdrawing wire tool can be used
in cooperation with the conductor gripper to tighten the conducting wire. Our
product is designed with the friction structure,whcin is flexible and reliable
to turn.
And
our steel double hook turnbuckle plays a role in
tightening the Steel Wire Rope, stranded steel wire, and some others. This
product from 14113 to 14116 can be also provided with the ring structure, which
must be clearly indicated in the contract. And the ratchet tackle block is always found in the line
construction. It serves to tighten up the stranded steel wire, and aluminum
stranded conductor, among others. The telescopic length reached 1 m.
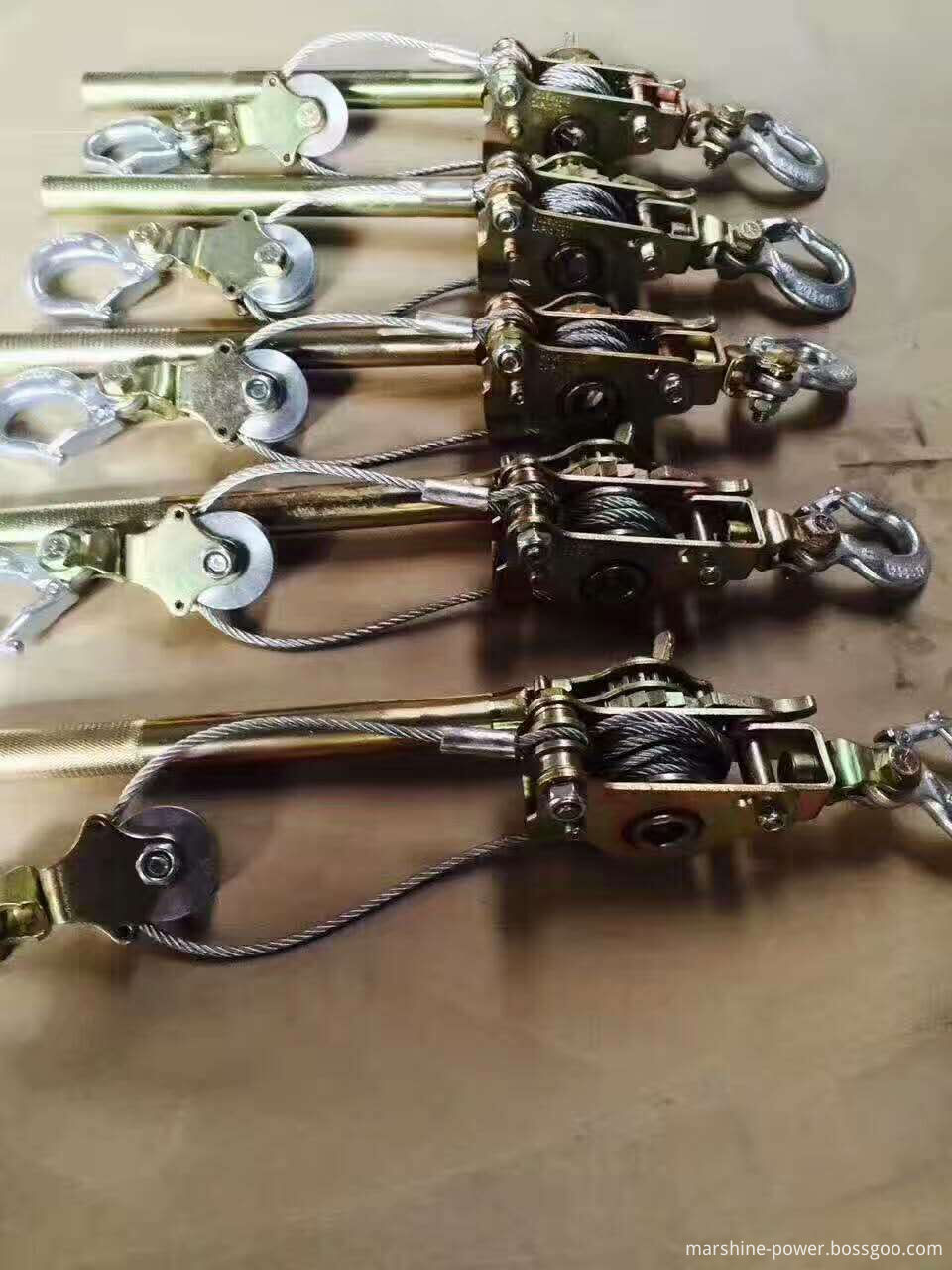

Ratchet Withdrawing Wire Tool,Cable Ratchet Tightener, Cable Tightener Rigging, Cable Turnbuckle Hardwares
NINGBO MARSHINE POWER TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD. , https://www.marshine-power.com