Chlorella zofingiensis Donz is a unicellular edible Chlorella that has the special mechanism of accumulating astaxanthin and oil as energy reserves for self-protection under difficult conditions. Astaxanthin is a unique structural keto carotenoid known as the strongest antioxidant in nature and has been widely used in medicine, food and aquaculture. Biomass energy based on high fat algae, such as biodiesel, is considered the most likely alternative to future oil. The study on the regulation of algae astaxanthin and oil synthesis has important and far-reaching significance.
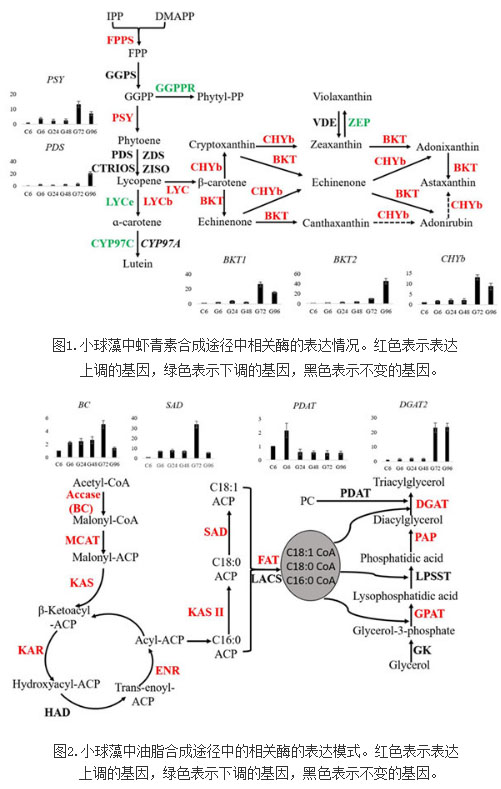
Recently, Huang Weiping, a doctoral student at the Kunming Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences, under the guidance of researcher Huang Junchao, conducted an in-depth study of the changes in the transcriptome and related metabolites of Chlorella under high glucose, high light, and other culture conditions. Chlorella was found to be involved in all genes involved in the synthesis of astaxanthin and lipids. It was found that the IPP of the precursor of astaxanthin in Chlorella was mainly derived from the MEP pathway, illustrating that it is different from the synthesis of astaxanthin in Haematococcus pluvialis. Pathways and regulatory mechanisms provide reliable theoretical guidance for the next step in the use of metabolic engineering to modify the algae to enhance its astaxanthin synthesis efficiency (Figure 1).
The study also found that the synthesis of chlorella oil mainly through the acyl-CoA pathway, most of the enzymes in the synthesis pathway have multiple coding genes, and the up-regulation of these genes under inducing conditions is positively correlated with the content of chlorella oils. (figure 2).
The results were published in Algal Research, a journal of algal research, under the title Transcriptome analysis of Chlorella zofingiensis to identify genes and their expressions involved in astaxanthin and triacylglycerol biosynthesis. The study was supported by the Yunnan Provincial Department of Science and Technology Fundamental Research Fundamental Project (Y43E531261).
ECB (blend ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer with asphaltic resin) waterproofing roll material is the first choice of domestic and overseas tunnel and dam waterproofing projects. It' s the ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer by two-section extrusion three-roller calendering manufacturing. belong to environmental protection material.

Performance Characteristics:
Flexibility, cold resistance, flexibility, stress crack resistance, light weight.
Executive Standard:
TB/T 3306.1-2014 GB18173.1-2012
Specification:
Thickness: 1.0-3.0mm Width: 1- 3m
Application:
Especially suitable for the waterproof material of dome inner surface. also can be used to tunnel lining , underground project various construction joints drainage and aterproof. and blind drain drainage.
ECB Waterproofing Roll Material
Ecb Waterproofing Roll Material,Ecb Waterproof Roll,Ecb Macromolecule Waterproof Roll,Ecb Waterproofing Roll
Shandong Tianhai New Materials Engineering Co., Ltd , https://www.chinatinhy.com