 Spring steel is widely used in aircraft, railway vehicles, automobiles, tractors and other transportation equipment and engineering machinery and other equipment. Spring steel should have excellent overall performance, and it is expected to obtain higher mechanical properties (especially elastic limit, strength limit, yield ratio), anti-reduction performance (ie, anti-regression performance, also called anti-relaxation performance), and fatigue performance. , hardenability, physical and chemical properties (heat resistance, low temperature resistance, oxidation resistance, corrosion resistance, etc.). At the same time, starting from the perspective of energy saving and economy, the requirement to reduce the weight of springs to reduce the weight of vehicles, motorcycles, and other transportation tools has also become an important aspect, and thus the requirements for the development of high-strength spring steels have been proposed. In recent years, a large amount of research work has been carried out at home and abroad in order to further improve the strength and service life of spring steel.
Spring steel is widely used in aircraft, railway vehicles, automobiles, tractors and other transportation equipment and engineering machinery and other equipment. Spring steel should have excellent overall performance, and it is expected to obtain higher mechanical properties (especially elastic limit, strength limit, yield ratio), anti-reduction performance (ie, anti-regression performance, also called anti-relaxation performance), and fatigue performance. , hardenability, physical and chemical properties (heat resistance, low temperature resistance, oxidation resistance, corrosion resistance, etc.). At the same time, starting from the perspective of energy saving and economy, the requirement to reduce the weight of springs to reduce the weight of vehicles, motorcycles, and other transportation tools has also become an important aspect, and thus the requirements for the development of high-strength spring steels have been proposed. In recent years, a large amount of research work has been carried out at home and abroad in order to further improve the strength and service life of spring steel. 1 Domestic and foreign major steel spring steel spring steel in China in the 1950s was reference to the former Soviet Union spring steel grade, mainly for the Si-Mn spring steel has the disadvantage of low hardenability, with the rapid development of the national economy, It can no longer meet the needs of China's industrial development. After two revisions in 1977 and 1984, some useless grades were removed and a high hardenability Cr-Mn spring steel was added. The spring steel currently used and listed in GB/T 1222-2007 has 15 steel types.
When ASTM A 689 spring carbon steel and alloy steel bar are classified by chemical composition, the standard steel grades are 100, 4100, 5100, 6100, 8600 and 9200 of AISI series, and include AISI boron steel series. 10B00, 15B00, 50B00, and 51B00. The specified steel grades are found in the standards ASTM A 322 and A 576, and the chemical composition of AISI steel grades can be adjusted to suit the specific steel size, spring shape, and permeability required for other special needs. For delivery by hardenability, the capital letter “H†should be added after the steel type. Standard alloy steel grades are the AISI series and 4100H, 5100H, 6100H, 8600H, and 9200H, and 50B00H and 51B00H including the AISI boron series. See ASTM A 304 for specified steel grades.
U.S. spring steels are of various types and quantities, but the commonly used steels are 9260, 9254, 5160, and improved 5160, and the 5160(H) and 9260 are the most widely used and the largest.
Japanese spring steel standard JIS G4801 comes with 9 steel types. When JIS G4801 was revised in 1984, spring steel SUP4 was removed due to its useless value, and SUP3 was only used as a supplement to the leaf springs of railway vehicles. Of the eight alloy spring steels, SUP6 and SUP7 are Si-Mn steels. The high-silicon SUP7 is mainly used for high-stress suspension springs; SUP9 and SUP9A are Cr-Mn steels; compared with SUP9, it was taken from the revised standard in 1977. American steel species SAE5160 SUP9A has higher carbon, manganese and chromium content, hardenability is also better, suitable for coarse suspension springs; SUP10 is Cr-V steel, steel toughness, suitable for use conditions Bad spring steel; SUP11A is a spring steel with boron treatment of SUP9, with better hardenability, can be used for 35 mm thick springs; two new brands were introduced in the new 1984 standard; SUP12 (SAE9254) It is Si-Cr steel with good tempering resistance and decarburization resistance and is used for high stress suspension springs. SUP13 (SAE4161) is Cr-Mo steel with very good hardenability and can be used for oversized springs over 60 mm in diameter. .
German spring steel standard DIN 17221** has 6 steel grades. Among them, 38Si7 is Si-Mn steel, 54SiCr6 and 56SiCr7 are Si-Mn-Cr steels, 55Cr3 is Cr-Mn steel, 50CrV4 is Cr-V steel, and 51CrMoV4 is added on the basis of 50CrV4 with a certain content of Mo, which greatly improves The hardenability and tempering stability of steel are suitable for the production of super-large springs that work in high temperature environments.
2 Production status of spring steel at home and abroad After more than 50 years of development, China's spring steel production has grown from nothing and has grown and achieved great progress. Shanghai Wugang, Taigang, Xingcheng Special Steel, Dongbei Special Steel and other companies have newly built or improved several advanced spring steel production lines in recent years. They adopt the “Electric furnace initial refining → LF refining furnace → VD vacuum degassing → Continuous casting → The "rolling" process produces various grades of alloy spring steel, which has made great progress in the production technology of spring steel. Some other companies have also shown strong development momentum, such as Jiangsu Shagang Huaigang Special Steel, Laiwu Special Steel, and Shigang. In particular, the market share of railway spring springs and fastener spring steel used by Huaigang Special Steel Corporation is 80%. However, there are also some spring steel producers that gradually shrink their steel output and become less and less competitive. The main reasons are the following:
(1) The quality and price of spring steel products lack market competitiveness. (2) The degree of product specialization is low and the variety structure is irrational.
(3) The spring steel production process and technical equipment are backward.
(4) The strength of research and development of advanced spring steel technology is weak. Foreign spring steel production started earlier and is more advanced than domestic ones in terms of production equipment, new technology, new technology research, and product quality control. For example, large steel furnaces are used for crude steel supply. Or blast furnace - converter process, in the use of electric furnace to do the initial furnace, the use of selected steel scrap, so as to ensure that the participating elements in crude steel is at a lower level; the use of powder-free dephosphorization of electric furnace slag tapping technology; Converter steel vacuum deslagging to reduce phosphorus content and prevent oxidation slag from entering the refining furnace; using RH vacuum degassing process on the basis of LF scouring; cross-sectional size of continuous casting billet is generally larger than domestic special steel mills, through large compression ratio Improve or eliminate some of the defects caused by casting, use multi-stage electromagnetic stirring to reduce continuous segregation and forging defects, and reduce segregation by using soft-pressing, large-diameter roll pressing and continuous forging and other liquid-phase hole pressing techniques; For heat treatment, it has a complete finishing heat treatment rotor and quality assurance system.
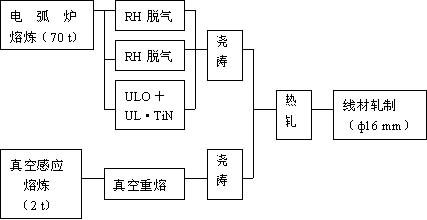
Tatung Special Steel Co., Ltd. uses the production process shown in Fig. 1 to produce ULO's SUP6, SUP7, and SUP120. The ULO treatment (ultra-low oxygen treatment Ultral Low Oxygen) concrete steps are as follows: in a more than the power alkaline arc furnace molten steel argon, after adding Fe-Si or Al to molten steel for pre-deoxidation, to obtain high alkalinity Reduction slag. Then the molten steel is poured into the ladle, and the legs of the RH cycle degassing device are inserted into the molten steel, and the molten steel is taken into the vacuum chamber of the degassing device. With the large-capacity jet pump, the vacuum degree is kept below 13.3 Pa, and a small flow of argon gas is introduced into the molten steel. The molten steel foams into the vacuum chamber. The deoxidation reaction of carbon in the molten steel rapidly proceeds and deoxidation of the molten steel is performed. When the carbon-oxygen reaction reaches equilibrium, Al deoxidizer is added. In order to promote the separation and removal of the deoxygenation products and to maintain the stability of the deoxidation state, the deoxygenation operation is continued, and finally the amount of Al added is adjusted. After the RH cycle degases, the oxygen content drops to about 15 mg/L. For example, to maintain the oxygen content of not more than 15 mg/L, the molten steel should be kept without oxidation during casting and solidification in order to avoid contamination and promote the removal of the deoxidation product.
In 1993, Thyssen company in Germany made an initial success in the inclusion control of Si-Cr valve spring steel. Although the steel still contains 10~15 μm inclusions, it does not exceed the spring manufacturer's maximum size of 15 μm. The request.
Brazil's Ipanema company developed in 1989 a vacuum deoxidation*VRSO treatment process for the production of ultra-low oxygen gate spring steels. The level of purity achieved by this process is higher than that achieved by conventional processes used in vacuum degassing (VD) systems, which can reduce the average total oxygen content in steel from 13.5 mg/L to 8.4 mg/L in conventional processes. The total amount of microscopic inclusions decreased by more than 2/3.
3 Development Trend of Spring Steel at Home and Abroad 3.1 The development of spring steel in high-strength direction Increasing spring design stress and reducing spring weight is the development direction of springs. The two main factors influencing the design stress of spring steel are the anti-fatigue and anti-emulsion properties. The new generation ultra-high strength spring steel has the following characteristics: 1 ultra-high strength; 2 ultra-high fatigue strength and corrosion fatigue performance; 3 excellent Anti-ballistic performance; 4 good economy.
To achieve this goal, we mainly use the following two approaches:
(1) Research and development of new steel grades. On the one hand, by optimizing the content of alloy elements in existing spring steels and adding them as alloying elements, on the other hand, they learn from the experience of ultra-high-strength steels for aviation to reduce carbon content and add V and Vb.
(2) Research and development of new thermal processing and heat treatment processes. With the existing steel grades basically unchanged, ultra-high strength is achieved through the research and development of processes such as deformation heat treatment, induction heat treatment, and on-line heat treatment. At present, foreign deformation heat treatment and induction heat treatment process have been used in actual production, and online heat treatment process is under research and development.
3.2 Development of spring steel to high-elastic defensive force line The main factor that determines the allowable stress of the spring is the anti-rejection force, so the focus of research and development of high-strength spring steel has been increased.
Resilience of the spring material is the ability of the material to resist plastic deformation or degraded load carrying capacity. If only from the perspective of the material itself, as an example to improve the resilience should start by selecting the right chemical composition, and then with the appropriate thermal processing and heat treatment, in order to obtain the ideal microstructure, grain size, second phase point and hardness, etc. .
Si is one of the most effective elements in increasing the resilience of alloying elements, and its role is second only to C. This is because Si has a significant effect of solid solution strengthening and can change the number, size, and morphology of precipitated carbides during tempering, thereby improving the tempering stability of the steel. Therefore, early spring steels with excellent ballistic resistance (design stress 1 000~1 100 MPa) are generally high in silicon content, such as SUP7, SUP12. However, the Si content of such steels as SUP7 and SAE9260 has reached the highest value, and it is difficult to improve the anti-reducing force by increasing the silicon content. If we want to develop new materials with better deterrence and good overall performance, we must find new ways. One of the important ways is to use precipitation strengthening and grain refining strengthening techniques, such as the addition of microalloying elements V and Nb.
3.3 Spring steel development towards high purity Domestic and foreign steel mills and automobile plants put forward very good requirements for the oxygen content of spring steels. For example, the Swedish SKF standard requires that the spring steel oxygen content is less than 15 μm. Spring steel production enterprises should start from the two aspects of smelting process and continuous casting process, and adopt measures such as strengthening raw material management, reasonable ingredients, concentrating raw materials into furnaces, strengthening smelting operations, optimizing smelting processes, improving deoxidation and slagging systems, and strengthening furnace refining and refining measures. , Produce high purity spring steel.
4 Conclusion The development of spring steel to high-strength, high-impact resistance and high purity is the current development direction of spring steel production and application.
Fig. 1 Ultra-pure spring steel production process of Datong Special Steel