When I was a child, the ground of the house was made of cement. In the summer, I sprinkled some water on it and drove the wind with a ceiling fan. It was quite cool. However, it will look a bit cold in the winter, so someone will put on the carpet to add some warmth. Nowadays, people decorate their houses, and the ground is more floor-to-wall. It is practical and beautiful, giving people a more gentle and comfortable feeling. Faced with a wide variety of wooden floors, many people do not know how to choose to match more with the room. Today, Qijia Xiaobian tells you.

First, pay attention to the mix of lighting and floor color
When comparing colors on a wooden floor, it is often because of the light source on the spot that wood floors that are not suitable for the room are mistakenly selected, and the main reason is the difference in space brightness. If you assess the family's lack of natural light, you should try to avoid buying too dark wood flooring, so that the entire space is too dark, not only to make the space narrow, but also produce a sense of visual pressure.
The bright space is less limited in the color of the wooden floor; however, if the lighting in the home is poor, avoid choosing dark floors.
Second, the floor color will also affect the room area
Color can cause people's visual effects, warm colors are expanding colors, and cool colors are shrink colors. Therefore, houses with small housing areas should be chosen from cool colors or simple and bright wooden floors, so that the sense of space can be expanded if warm-colored rice floors are used. If you do, it will look more narrow and increase the sense of oppression. If the room is large enough and there is plenty of natural light, you can choose a dark, coarse-grained wooden floor, and avoid large and chaotic patterns.

Third, according to the room function to choose
Different types of space are available, and the types of wood floors that apply are also different. For example, the bedroom will usually choose warm or neutral wood floors, giving people a quieter, warmer feeling. And if it is a children's room or a game room, we must pay attention to the wear resistance of wood flooring, such as children wear toys, the game is not easy to damage the super wear-resistant wood flooring, is a very good choice.
Fourth, choose according to the direction of the room
The east-facing room darkens the room earlier because sunlight is also earliest. It is often safest to use light and warm colors. The south-facing rooms have the longest hours of sunshine. The use of cold-coloured wooden floors often makes people feel more comfortable and the rooms are more charming. The west-facing room seems to be more comfortable because of the influence of the western sunset, the strongest sunset in the day, and the use of deep-frozen wood floors. The north facing room has no direct sunlight, so you should prefer to use a warm wood floor with a lighter shade.

V. Different mental ages choose differently
The choice of wooden floor patterns and colors is related to people's age. The younger ones will choose bright colors and strong visual impact colors to reflect their publicity. Most people in the mature stage will choose wood floors that are lighter in color and lighter in color. They will be more style-conscious, but they will still prefer bright colors in their colors. Those who enter middle age prefer a thick, stable, atmospheric wood floor.
Wooden floor home knowledge
Product List
|
aluminium trihydrate (ATH) |
21645-51-2 |
|
magnesium hydroxide (MDH) |
1309-42-8 |
|
antimony trioxide (ATO) |
1309-64-4 |
|
Zinc borate |
1332-07-6 |
|
Melamine polyphosphate (MPP) |
218768-84-4 |
|
Melamine phosphate (MP) |
20208-95-1 |
|
Melamine Cyanurate(MCA) |
37640-57-6 |
|
68333-79-9 |
Introduction
The most common inorganic flame retardants are the hydroxides or aluminium and magnesium. Aluminium trihydroxide (ATH) is by far the most widely used Flame Retardant on a tonnage basis. It is inexpensive, but usually requires higher loadings in polymers of up to more than 60%, because the flame retardant mechanism is based on the release of water which cools and dilutes the flame zone. Magnesium hydroxide (MDH) is used in polymers which have higher processing temperatures, because it is stable up to temperatures of around 300 C versus ATH which decomposes around 200 C.

Fine precipitated ATH and MDH (grain size < 2um) are used in melt compounding and extrusion of thermoplastics like cable PVC or polyolefins for cables. For use in cable, ATH and more often MDH are coated with organic materials to improve their compatibility with the polymer. Coarser ground and air separated grades can be used in liquid resin compounding of thermosets for electrical applications, seats, panels and vehicle parts.
A number of other inorganic substances show flame retarding effects and are used in commercial applications. Most of them are used as synergists i.e. they enhance the performance of other flame retardants or they are used for specific effects like the suppression of smoke formation. For example, borates are used as mixtures of boric acids and borax as flame retardants for cellulose (cotton) and of zinc borate for PVC and other plastics like polyolefins, elastomers, polyamides, or epoxy resins. In halogen-containing systems, zinc borate is used in conjunction with antimony oxide, while in halogen-free systems it is normally used in conjunction with aluminium trihydroxide, magnesium hydroxide, or red phosphorus. In some particular applications zinc borate can be used alone. Boron containing compounds act by stepwise release of water and formation of a glassy coating which protects the surface.
Zinc compounds were initially developed as smoke suppressants for PVC (Zinc hydroxystannate). Later it was found that they also act as flame retardants in certain plastics mainly by promoting char formation.
Intumescent Flame Retardant systems expand to produce foams. They are used as coatings not only to protect combustible materials such as wood and plastics, but also steel structures in buildings, because steel loses its strength when exposed to high temperatures in a fire. The intumescent effect is achieved by combining an acid source like ammonium polyphosphate, a source of carbon, compounds which release noncombustible gases for blowing the foam on thermal decomposition and resin binders to stabilise the foam.
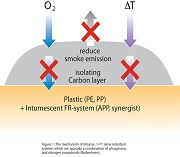
Expandable graphite is manufactured from flake graphite by treatment with strong acids like sulphuric or nitric acid. The acid is trapped in the crystal layers of the graphite ("intercalated"). When it is heated, the graphite starts to expand up to several hundred cm3 per gram, forming a protective layer for the polymer. Expandable graphite is used in plastics, rubbers (elastomers), coatings, textiles and especially in polymeric foams. To achieve an optimum flame retarding effect, the use of synergists like ammonium polyphosphate or zinc borate is often necessary. The black colour of graphite limits its applicability in some cases.
Nanocomposites have been gaining increasing attention since the late 1990s as potential new flame retardants. Nanocomposites
are polymer layered silicates based on aluminosilicate clay minerals like montmorillonite, composed of layers with gaps (gallery spaces) in between. These silicates have the ability to incorporate polymers. Research with nanocomposites has focused on plastics like polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA), polypropylene, polystyrene, and polyamides. Nanocomposites particularly prevent dripping and promote char formation. Therefore, they have been used as synergists in some polymer / flame retardant combinations. However, they require special processing and for the time being are not considered to become viable stand-alone flame retardants.
Other inorganic fillers like talcum or chalk (calcium carbonate) are sometimes denoted as flame retardants, but they do not specifically interact with the ignition process. On the contrary, simply by diluting the combustible polymer they reduce its flammability and fire load.
Inorganic Flame Retardant Additives, Inorganic Flame Retardant Polymers, Inorganic Flame Retardant Chemicals,Ammonium Polyphosphate
Shandong Novista Chemicals Co.,Ltd (Novista Group) , https://www.novistachem.com